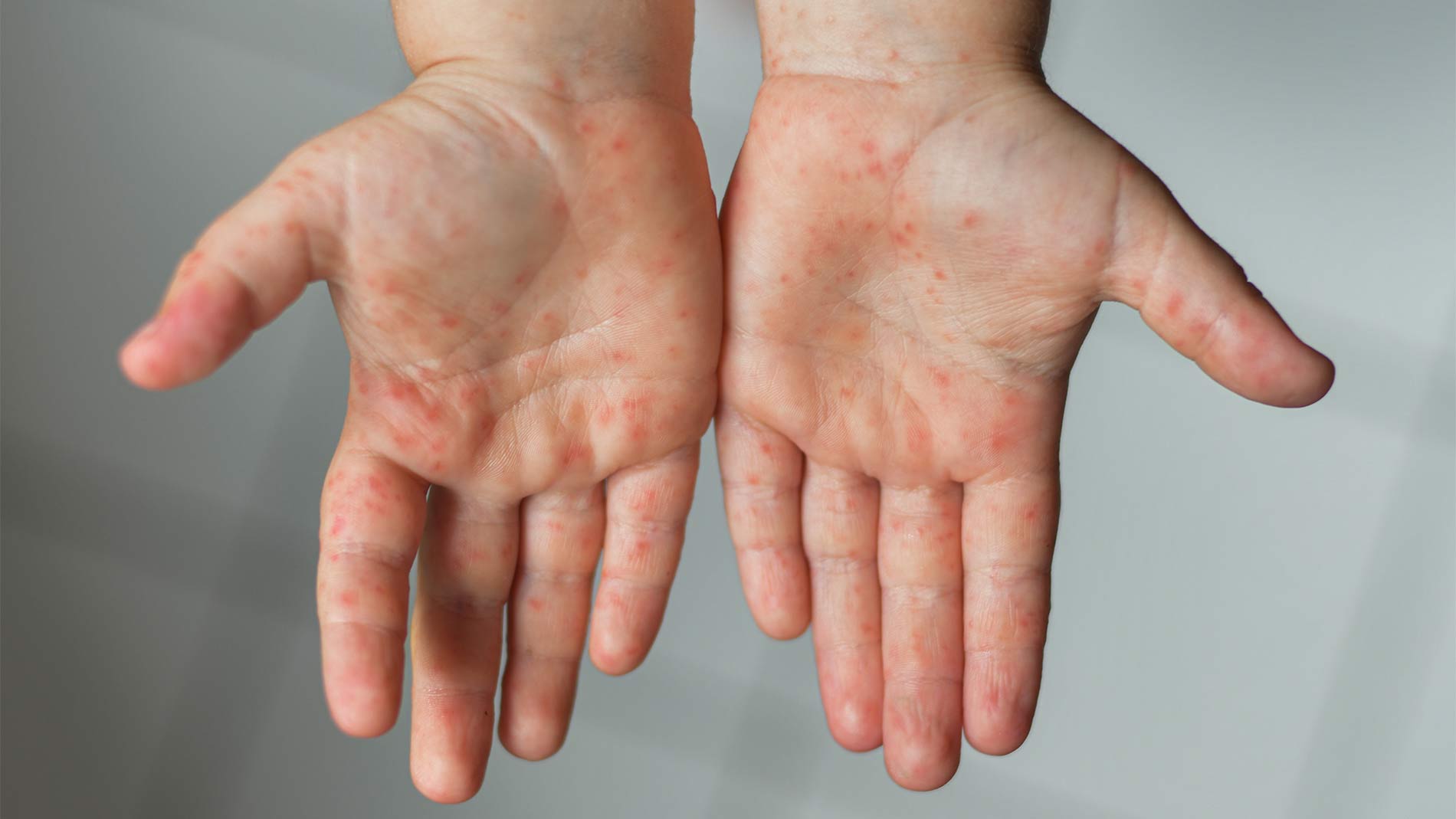
Summary; Davin’s Tips.
Here are my favourite go to tips on how to treat hand eczema:
- Soap & detergents: Switching to mild, fragrance-free soaps and detergents can help reduce symptoms.
- If you’re in cold weather, apply thick, fragrance-free moisturizer to the hands for hydration and wear gloves to protect your hands from cold and dry air.
- Topical corticosteroid creams work well at reducing inflammation and itching.
- Over the counter oral antihistamines can relieve itching and inflammation.
- For more severe cases, phototherapy light therapy can help to reduce inflammation and itching.
What causes hand eczema?
Hand eczema is a common condition that is characterized by dry, itchy, red, and cracked skin on the hands. There are several causes of hand eczema, including:
- Genetics: A family history of eczema can increase the risk of developing hand eczema.
- Allergies: Exposure to allergens such as certain foods, metals, fragrances, or chemicals can trigger hand eczema.
- Irritants: Repeated exposure to irritating substances such as soap, water, detergents, or solvents can lead to hand eczema.
- Stress: Stress and anxiety can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of developing hand eczema.
- Climate: Exposure to extreme temperatures, such as cold or dry weather, can dry out the skin and cause hand eczema.
- Contact dermatitis: This is a type of eczema that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritating substance, such as poison ivy or latex.
- Infection: In some cases, hand eczema may be caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
It’s essential to identify the underlying cause of hand eczema and take steps to manage or eliminate exposure to triggers to prevent flare-ups. If you experience symptoms of hand eczema, you should consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How do you treat genetically caused hand eczema?
Genetically caused hand eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, can be a chronic and difficult condition to manage. While there is no known cure for atopic dermatitis, there are various treatment options available that can help to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Here are some possible treatments for genetically caused hand eczema:
- Moisturize regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized is key to managing hand eczema. Use a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer throughout the day, especially after washing your hands.
- Avoid irritants: Identify and avoid any triggers that can make your eczema worse, such as harsh soaps, detergents, and cleaning products. Wear gloves when using chemicals or doing wet work.
- Topical corticosteroids: Your doctor may prescribe topical corticosteroids, which can help to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. These should be used only as directed by your doctor and for a limited time.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors: These medications can help to reduce inflammation and itching, and may be an alternative to corticosteroids.
- Oral antihistamines: These may be used to relieve itching and help you sleep better at night.
- Phototherapy: Light therapy can help to reduce inflammation and itching. Your doctor may recommend this treatment if your eczema is severe and doesn’t respond to other treatments.
- Systemic medications: In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe oral medications to help control inflammation.
What is contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that irritates it or causes an allergic reaction. There are two types of contact dermatitis: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
Let’s talk about irritant contact dermatitis:
Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when the skin is exposed to a substance that damages the outer layer of the skin. This can happen after exposure to substances such as soaps, detergents, acids, or alkalis. Symptoms of irritant contact dermatitis may include redness, swelling, itching, and dry or cracked skin. In some cases, blisters may develop.
Hand eczema can be caused or exacerbated by a wide range of irritants, depending on individual sensitivity. Some of the most common irritants that can trigger hand eczema include:
- Harsh soaps and detergents: Harsh soaps and detergents can strip the skin of its natural oils and cause dryness, irritation, and itching. Switching to mild, fragrance-free soaps and detergents can help reduce symptoms.
- Water: Frequent exposure to water, especially hot water, can strip the skin of its natural oils and lead to dryness and irritation.
- Solvents: Exposure to solvents and chemicals, such as those found in cleaning products, paints, and pesticides, can irritate the skin and cause eczema. Wearing gloves and protective clothing can help reduce exposure to these irritants.
- Metals: Some people may develop eczema after coming into contact with metals such as nickel, cobalt, or chromium.
- Water: Frequent or prolonged exposure to water can cause dryness and irritation of the skin, which can worsen eczema symptoms. It’s important to moisturize the hands regularly and avoid excessive hand washing or immersion in water.
- Certain foods: Some people with eczema may experience flare-ups after eating certain foods, such as dairy products, eggs, nuts, and soy.
- Weather: Exposure to cold and dry air can cause dryness and irritation of the skin, which can worsen eczema symptoms. Wearing gloves and using a humidifier can help protect the skin from these environmental factors.
By avoiding these irritants, individuals with hand eczema can help prevent flare-ups and reduce the severity of symptoms. If you are unsure about which irritants may be triggering your eczema, a dermatologist or healthcare provider can help you identify them and develop a plan to manage your symptoms.
Let’s talk about allergic contact dermatitis:
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that triggers an allergic reaction. Common allergens include nickel, latex, fragrances, and certain chemicals found in cosmetics, soaps, and cleaning products. Symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis may include redness, swelling, itching, and the development of a rash or blisters. These symptoms may take several days to appear after exposure to the allergen.
Some of the most common allergies that can trigger hand eczema include:
- Contact allergies: These are caused by coming into contact with a substance that the body is allergic to, such as nickel, latex, or certain chemicals found in cosmetics, soaps, and cleaning products.
- Food allergies: Some people with eczema may experience flare-ups after eating certain foods, such as dairy products, eggs, nuts, and soy.
- Seasonal allergies: Allergies to pollens, mold, and other environmental allergens can cause hand eczema in some people.
- Medication allergies: Certain medications can cause an allergic reaction that leads to hand eczema.
Treatment for allergic contact dermatitis may include avoiding the allergen, taking antihistamines, or using topical or systemic medications to manage symptoms. Your doctor or a dermatologist can help you determine which allergens may be causing your symptoms and recommend tests or other diagnostic tools to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the link between stress and hand eczema?
Stress is a common trigger for hand eczema in some people. Stress can affect the body’s immune system and lead to inflammation, which can worsen eczema symptoms. Stress can also cause people to engage in behaviors that can irritate the skin, such as scratching, rubbing, or picking at the affected areas. Additionally, stress can cause people to neglect self-care, such as moisturizing, which can worsen dryness and lead to more severe eczema symptoms.
While stress can trigger hand eczema, it’s important to note that eczema is a complex condition and is often influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Therefore, managing stress alone may not be enough to control eczema symptoms. However, reducing stress can be an important component of an overall treatment plan for eczema. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and other stress-reduction techniques may be helpful for some people with eczema. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that takes into account all of the factors that may be contributing to eczema symptoms.
How do you know if eczema is caused by a bacterial infection?
Eczema can sometimes be complicated by a bacterial infection, which can cause additional symptoms and may require specific treatment. Some signs that eczema may be complicated by a bacterial infection include:
- Presence of pus or discharge: If there is pus or discharge present in the affected area, this may indicate a bacterial infection.
- Worsening of symptoms: If eczema symptoms suddenly worsen or become more severe, this may indicate an infection.
- Crusting or oozing: If the skin becomes crusted or begins to ooze, this may indicate an infection.
- Increased redness and swelling: If the affected area becomes more red and swollen than usual, this may indicate an infection.
- Fever or chills: If you develop a fever or chills along with eczema symptoms, this may indicate a bacterial infection.
If you suspect that your eczema may be complicated by a bacterial infection, it’s important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider may recommend tests to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe antibiotics or other medications to treat the infection. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and to continue treatment for the full course of medication, even if symptoms improve.
When should you seek professional help for hand eczema?
You should seek professional help for hand eczema if:
- Your symptoms are severe: If your symptoms are severe, such as intense itching, redness, swelling, cracking, or bleeding, it’s important to seek medical attention. Severe symptoms can indicate a more serious underlying condition and may require specialized treatment.
- Your symptoms are not responding to treatment: If you have been treating your eczema at home but your symptoms are not improving or are getting worse, it’s important to see a healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can evaluate your condition and recommend additional treatment options.
- Your eczema is interfering with daily activities: If your eczema is interfering with your ability to perform daily activities, such as work, school, or household tasks, it’s important to seek professional help. Your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan that will help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
- You suspect an infection: If you suspect that your eczema may be complicated by a bacterial or fungal infection, it’s important to seek medical attention. Infections can worsen eczema symptoms and may require specialized treatment.
- You have other health conditions: If you have other health conditions, such as allergies or asthma, that may be contributing to your eczema, it’s important to seek professional help. Your healthcare provider can help you manage these conditions and develop a treatment plan that takes into account all of your individual needs.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or concerns, it’s important to seek professional help. A healthcare provider or dermatologist can evaluate your condition, recommend appropriate treatment options, and help you manage your eczema symptoms.
How can a dermatologist help hand eczema?
A dermatologist can help with hand eczema in several ways:
- Diagnosis: A dermatologist can accurately diagnose hand eczema by examining the affected skin and asking questions about symptoms and medical history. They can also perform tests to rule out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms.
- Treatment: A dermatologist can develop a personalized treatment plan based on the severity and underlying cause of the hand eczema. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, phototherapy, or biologic medications. A dermatologist can also recommend lifestyle changes, such as avoiding irritants or allergens and using gentle skin care products.
- Prevention: A dermatologist can provide advice on how to prevent hand eczema from flaring up. This may include avoiding known triggers, using moisturizers regularly, and taking steps to protect the hands from irritants.
- Management: A dermatologist can help manage long-term hand eczema symptoms and prevent complications such as infection or scarring. They can also provide ongoing monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
Overall, a dermatologist can play a critical role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of hand eczema. They can provide specialized care and guidance to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.